CE certification guide
CE certification is essential for ensuring that a machine complies with the relevant EU safety, health, and environmental requirements. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to CE certify a machine. Please use the following steps as a guideline for completing your own CE certification, which primarily focuses on traceability and manufacturer liability. This guide was created by Mad Plastic (https://www.mad-plastic.com/) and reviewed by l’Atelier des Recycleurs Fous (https://www.atelierdesrecycleursfous.fr/). The manufacturer is solely responsible for identifying the relevant risks and assessments for their machines. Mad Plastic and l’Atelier des Recycleurs Fous cannot be held liable for any incorrect or outdated information in this guide
More Information
1
Identify Applicable Directives
Determine which EU directives apply to your machine. Common directives for machinery include the Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC), the Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Directive (2014/30/EU), and the Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU).
This list is not exclusive and other directive might apply for some specific applications.

2
Understand Essential Requirements
Study the essential health and safety requirements (EHSRs) of each applicable directive. This is crucial for ensuring that your machine design complies with these requirements.

3
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC part 1
The Machinery Directive sets out essential health and safety requirements (EHSRs) that machinery must meet to be placed on the market within the EU. The EHSRs are divided into several categories:
General Requirements
Machinery must be designed and constructed to be safe and reliable throughout its lifecycle.
The design should consider ergonomic principles to minimize operator fatigue and discomfort.
Design and Construction
Stability and strength: Machinery must be stable during use, transport, assembly, and dismantling.
Risk reduction: Manufacturers must reduce risks by designing machinery that avoids or reduces hazards.
Controls: Machinery must have control systems that are safe, reliable, and accessible to the operator.

4
Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC part 2
Protection Against Mechanical Hazards
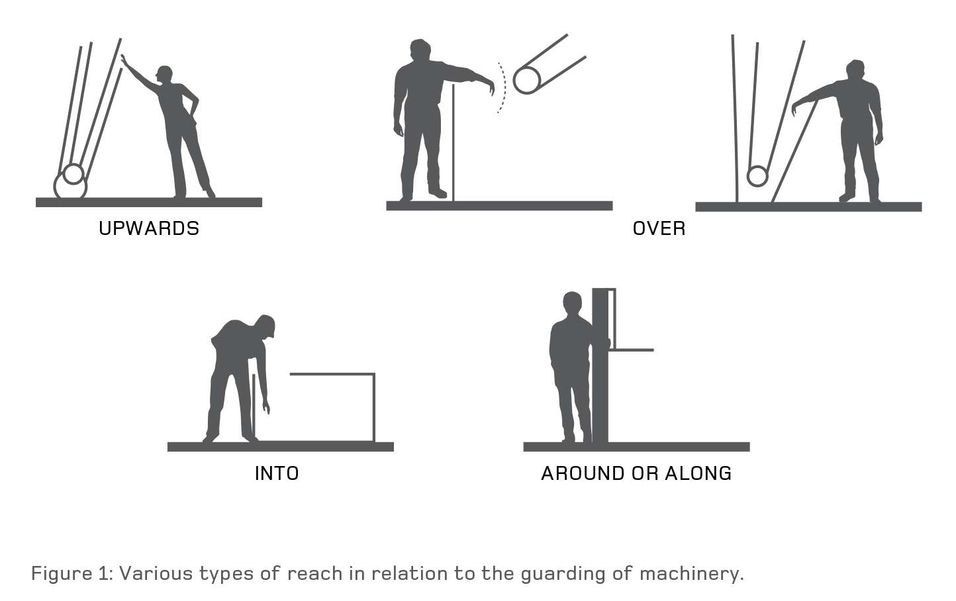
Guards and protective devices: Machinery must have protective measures to prevent access to dangerous parts.
Moving parts: The design must ensure that moving parts do not pose a risk to the operator or others.
Protection Against Other Hazards
Electrical hazards: Machinery must be designed to protect against electric shock and other electrical risks.
Noise and vibrations: Measures must be taken to reduce noise and vibration to acceptable levels.
Emissions: Machinery must minimize emissions of hazardous substances.
Maintenance and Instruction
Maintenance: Machinery must be designed to facilitate safe maintenance operations.
Instructions: Comprehensive and understandable instructions must be provided, covering safe use, maintenance, and disposal.
5
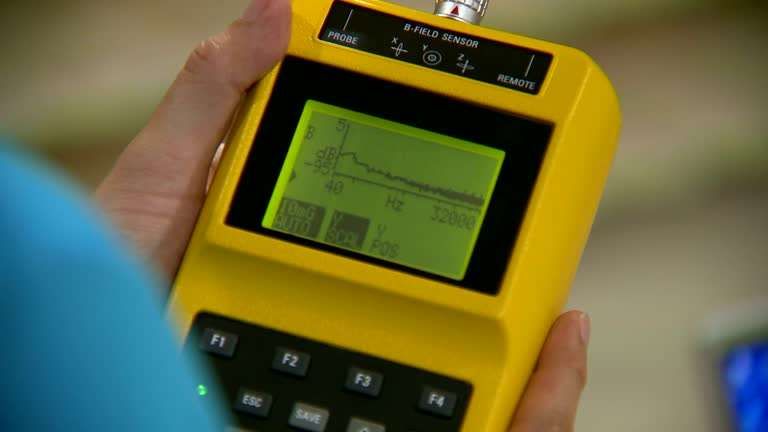
Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 2014/30/E
The EMC Directive ensures that electrical and electronic equipment does not generate, or is not affected by, electromagnetic disturbance.
Protection Requirements:
Emission: Equipment must not emit electromagnetic disturbances that exceed specified levels.
Immunity: Equipment must have adequate immunity to electromagnetic disturbances to operate as intended.
Technical Documentation:
Test reports: Documentation must include test results demonstrating compliance with emission and immunity requirements.
Risk assessment: An analysis of potential electromagnetic disturbances and mitigation measures.

6
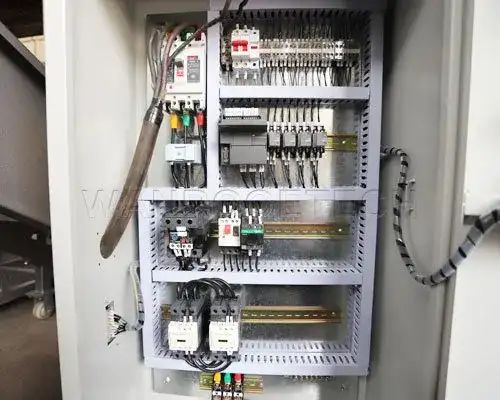
Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
The Low Voltage Directive applies to electrical equipment operating within certain voltage limits (50-1000 V AC and 75-1500 V DC).
Safety Objectives:
General conditions: Equipment must be designed and constructed to ensure protection against electrical hazards.
Protection against hazards: Measures must be taken to prevent electric shock, high temperatures, arcs, radiation, and mechanical hazards.
Insulation and protection: Adequate insulation and protective measures must be provided to ensure safety.
These safety objectives can be achieved by implementing the following measures:
Leaving 60% of the cabinet space empty to ensure adequate airflow and reduce the risk of overheating.
Using a standardized color code for wiring (e.g., yellow/green for grounding, light blue for neutral, red or white for control circuits, and black, brown, or grey for power lines).
Clearly labeling both ends of all cables.
Providing clear identification for all components within the cabinet.

7
Conduct Risk Assessment
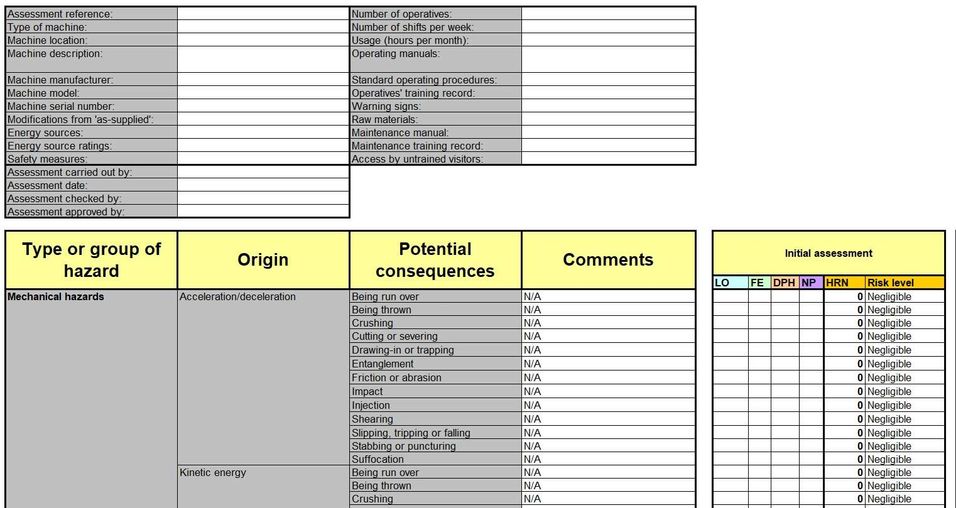
Perform a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential hazards associated with the machine. Use standards such as EN ISO 12100 to guide this process.
We have included a risk analysis calculator in the download set. This template contains a (non-exhaustive) list of potential risks that a machine might have. The manufacturer can select the relevant risks and document the measures taken to minimize them. These measures may already be incorporated into the Precious Plastic open-source design or added by the manufacturer.
In some cases, risks cannot be fully avoided. Then, warning stickers should be placed in relevant locations on the machine.


8
Apply Harmonized Standards
Harmonized European standards provide a presumption of conformity with the relevant EHSRs. Applying these standards simplifies the CE marking process. Check the latest list of harmonized standards for your applicable directives.
Hereunder a (non-exhaustive) list of potentially applicable standard :
EN ISO 12100:2010: Safety of machinery - General principles - Risk assessment and risk reduction
EN 60204-1:2018: Safety of machinery - Electrical equipment
EN ISO 13849:2015: Safety-related parts of control systems
EN ISO 13857:2019: Safety distances to prevent hazard zones
EN ISO 14120:2015: Guards
EN ISO 14119:2013: Interlocking devices associated with guards
EN 746-1:1997+A1:2009: Common safety requirements for industrial thermo-processing equipment
EN ISO 13732:2008: Methods for the assessment of human responses to contact with surfaces
EN 201:2009: Injection molding machines - Safety requirements
EN 1114-1:2011+A1:2013: Safety requirements for extruders

9
Technical Documentation
Compile a technical file that includes:
Detailed design and manufacturing drawings
A list of the standards applied
Results of design calculations and tests
A risk assessment report
A copy of the instructions for the machine (in English and/or the language of the country the machine will be installed)
Testing report template
EC Declaration of Conformity draft

10
Conformity Assessment
Depending on the directive, conduct the necessary conformity assessment procedures. This might involve internal production control, or it might require the involvement of a notified body for certain high-risk machines. We recommend always consulting a notified body for guidance with your first produced machine. They will review your risk assessment and documentation and determine if you can proceed with internal production control.

11
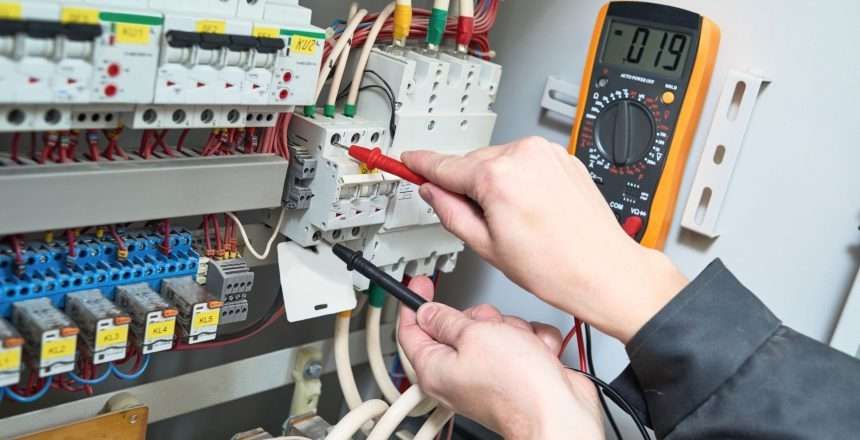
Testing
Perform or arrange for the necessary testing to ensure compliance with relevant standards and directives. This can include electrical safety, EMC, noise, and other specific tests based on the type of machinery. Depending on the results of your conformity assessment in step 10, these tests can be performed by your internal quality control department or shall be outsourced to a certified third party.

12
Compile the EC Declaration of Conformity
This is a formal statement declaring that the machine meets all relevant directives and standards. It must include:
Manufacturer’s name and address
Machine description
Directives and standards applied
Identification of the signatory empowered to bind the manufacturer
Place and date of the declaration
Please note that some machines require a certificate of conformity, which can only be provided by a notified body. Your conformity assessment in step 10 will determine whether a certificate of conformity is required.

13
Affix the CE Marking
Once conformity is confirmed, affix the CE marking to the machine. Ensure it is visible, legible, and indelible. The CE marking indicates that the machine complies with the applicable EU directives.
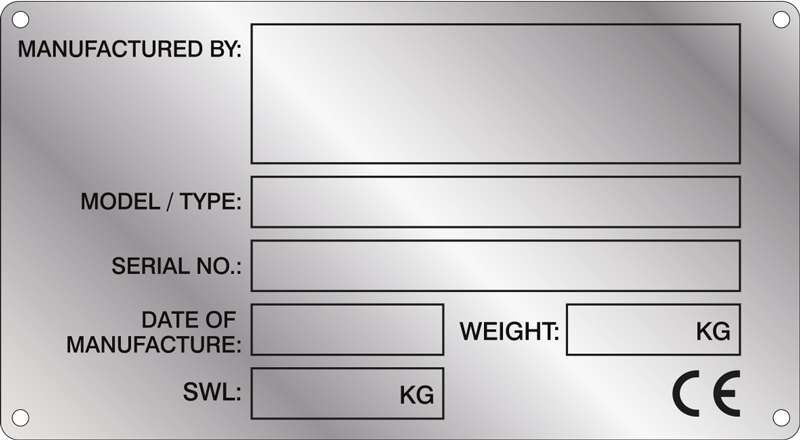
The CE marking shall be applied in a way it cannot be removed from the machine and contains at least :
CE Marking
The CE symbol.
Identification number of the notified body (if applicable).
Manufacturer Information
Name and full address of the manufacturer.
Contact information (phone number, email address).
Machine Identification
Model designation.
Serial number.
Year of manufacture.
Technical Specifications
Rated power (in kW or HP).
Voltage (in V).
Frequency (in Hz).
Operating pressure (IA).
Safety and Compliance Information (IA)
Any relevant safety marks or symbols.
Protection class (IP rating...).
Hazard warnings or symbols (IA).
Operational Information
Speed (in RPM, IA).
Capacity or throughput (IA).
14
Maintain Records
Keep all technical documentation and the EC Declaration of Conformity (step 7, 11 and 12), as well as all the relevant technical documentation (technical drawings, electric schematics...) for at least ten years after the machine is placed on the market. This documentation must be available to the relevant national authorities upon request.
